windows 10 & Python 3.5
1.下载graphviz-2.3.8.msi并安装,官网:http://www.graphviz.org/Download_windows.php
添加环境变量:C:\Program Files (x86)\Graphviz2.38\bin
2.pip install graphviz (0.7)
3.pip install pydot (1.2.3)
可视化结果: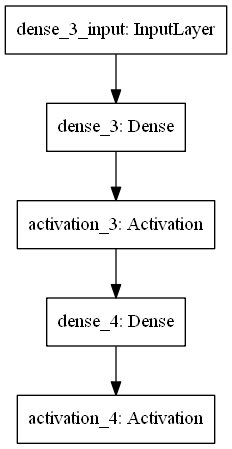
Ubuntu 16.04 & Python 2.7
1.sudo pip install graphviz (0.7)
2.sudo apt-get install graphviz (2.38.0-16)
3.sudo pip install pydot==1.1.0 (1.2.3的版本find_graphviz函数会报错)
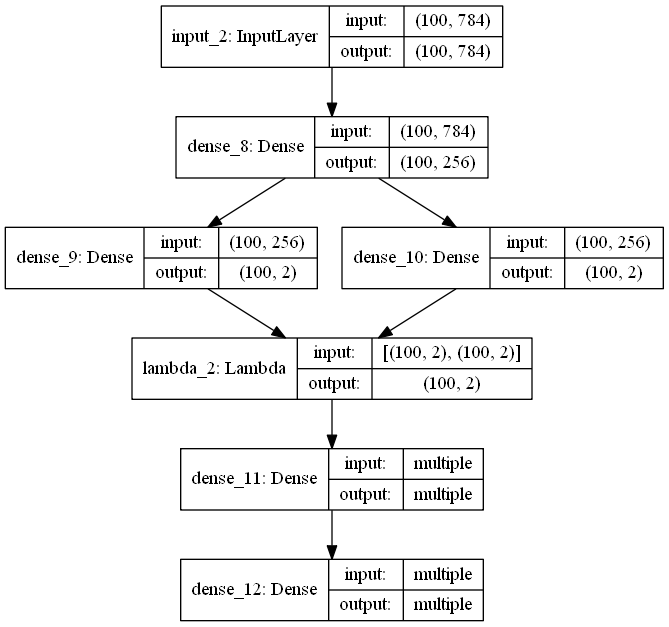
来个VAE网络试试:
可视化结果: